Cisco Viptela SD-WAN uses an overlay network architecture to connect geographically distributed sites securely and efficiently. This architecture separates the physical transport network (underlay) from the virtual network (overlay), enabling flexibility, scalability, and centralized control. The overlay network consists of secure tunnels that link sites across various transport types like MPLS, broadband, LTE, or satellite, forming a unified and secure SD-WAN fabric.

- January 28, 2025
- akil
- SDWAN
- No Comments
Understanding Cisco Viptela's Overlay Network Architecture
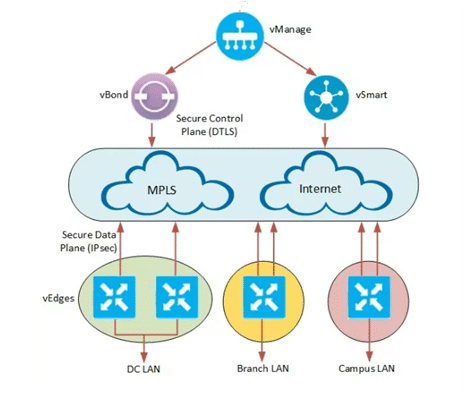
Key Components of the Overlay Network Architecture
- vManage (Management Plane)
- Role: Centralized controller that provides an interface for configuring, monitoring, and managing the entire SD-WAN network.
- Functions:
- Policy configuration and distribution.
- Real-time monitoring of devices and traffic flows.
- Automation of device onboarding with Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP).
2.vSmart Controllers (Control Plane)
- Role: Acts as the control plane, managing routing and policy distribution across the network.
- Functions:
- Distributes routing information to vEdge devices using OMP (Overlay Management Protocol).
- Enforces security and segmentation policies.
- Facilitates secure communication between devices by authenticating connections.
3. vBond Orchestrator (Orchestration Plane)
- Role: Facilitates the initial setup and secure onboarding of devices into the SD-WAN fabric.
- Functions:
- Authenticates vEdge devices, vSmart controllers, and vManage.
- Establishes the first connectivity between SD-WAN components.
- Assigns devices their respective roles in the overlay.
4. vEdge Routers (Data Plane)
- Role: Resides at the network edge and handles traffic forwarding.
- Functions:
- Establishes secure IPsec tunnels with other vEdge devices for end-to-end encryption.
- Routes traffic dynamically based on policies and real-time network conditions.
- Provides transport independence by supporting MPLS, broadband, and LTE.
How the Overlay Network Works
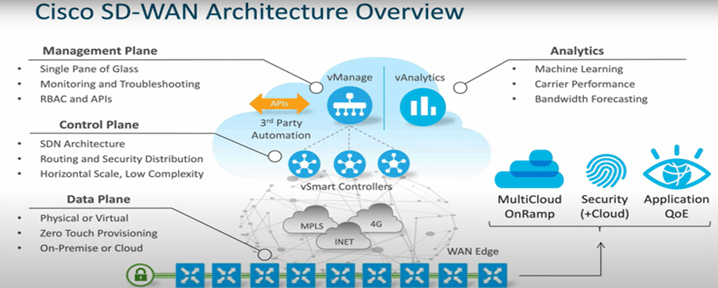
- Separation of Planes
The architecture divides the network into three planes:
- Management Plane: Oversees configuration, monitoring, and control.
- Control Plane: Handles routing information and policy distribution.
- Data Plane: Manages the actual forwarding of user traffic.
2.Secure Tunnels
Each site in the network communicates through encrypted IPsec tunnels, forming a secure overlay that operates independently of the physical underlay network.
3. Overlay Management Protocol (OMP)
OMP is a proprietary protocol that facilitates communication between the control plane (vSmart) and data plane (vEdge routers).
- Advertises routes, policies, and key information to maintain the overlay network.
- Ensures consistent routing and segmentation across all sites.
Features of Cisco Viptela's Overlay Network Architecture
- Transport Independence
- Works over multiple transport types (MPLS, broadband, LTE, satellite).
- Enables businesses to use cost-effective connections without sacrificing performance.
2. End-to-End Security
- Uses IPsec encryption for all traffic across the overlay.
- Enforces security policies centrally through vSmart controllers.
3. Scalability
- Supports thousands of devices across geographically dispersed locations.
- Easily integrates new sites with minimal configuration through Zero-Touch Provisioning.
4. Dynamic Path Selection
- Monitors performance metrics (latency, jitter, packet loss) to route traffic dynamically.
- Ensures optimal application performance by leveraging the best available paths.
5. Traffic Segmentation
- Creates isolated virtual networks (VPNs) within the overlay for secure segmentation.
- Supports different business units or applications with separate logical paths.
Advantages of the Overlay Network Architecture
- Flexibility:
- Decouples network operations from physical transport, enabling seamless deployment and management.
- Cost Efficiency:
- Reduces reliance on expensive MPLS circuits by integrating affordable broadband and LTE connections.
- Enhanced Performance:
- Application-aware routing and dynamic path selection improve user experience.
- Simplified Management:
- Centralized control and monitoring reduce operational complexity.
- Resilience:
- Ensures uninterrupted connectivity with automatic failover and redundancy mechanisms.
Overlay vs. Underlay Network
| Aspect | Overlay Network | Underlay Network |
| Definition | Virtual network connecting sites | Physical transport network (MPLS, broadband, LTE) |
| Encryption | End-to-end IPsec encryption | No encryption by default |
| Routing | Policy-driven and dynamic | Static or manually configured |
| Management | Centralized (vManage, vSmart) | Decentralized |
| Transport | Independent of transport | Dependent on physical links |
Real-World Use Case
A retail chain with 500 branches uses Cisco Viptela SD-WAN to:
- Connect branches securely over broadband and LTE, reducing MPLS costs.
- Ensure high availability with dynamic path selection during network congestion or outages.
- Segment traffic for POS systems, guest Wi-Fi, and corporate communications using VPNs.
Conclusion
Cisco Viptela’s overlay network architecture redefines modern WAN management by offering a secure, flexible, and centralized approach. By abstracting the physical transport network, it allows businesses to focus on application performance, security, and cost efficiency. With its scalable and resilient design, it supports digital transformation efforts, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving networking demands effortlessly.

